¶ Connecting your devices to Hive
Hive is a cloud-first network management tool that allows you to manage and visualize your entire Meshmerize network in a centralized manner.
Connecting a device to your Hive is done in two steps:
- Configure your device to connect to YOUR Hive instance.
This is done either through the built-in Web UI of the device or through the command line. For this, the Hive Worker needs to be enabled, and the MQTT Host must be set to the domain name of your Hive instance. For detailed instructions for your device, see one of the following sections:- Configuration on MeshmerizeOS UI.
- Configuration on Acksys WaveOS UI.
- Command line configuration.
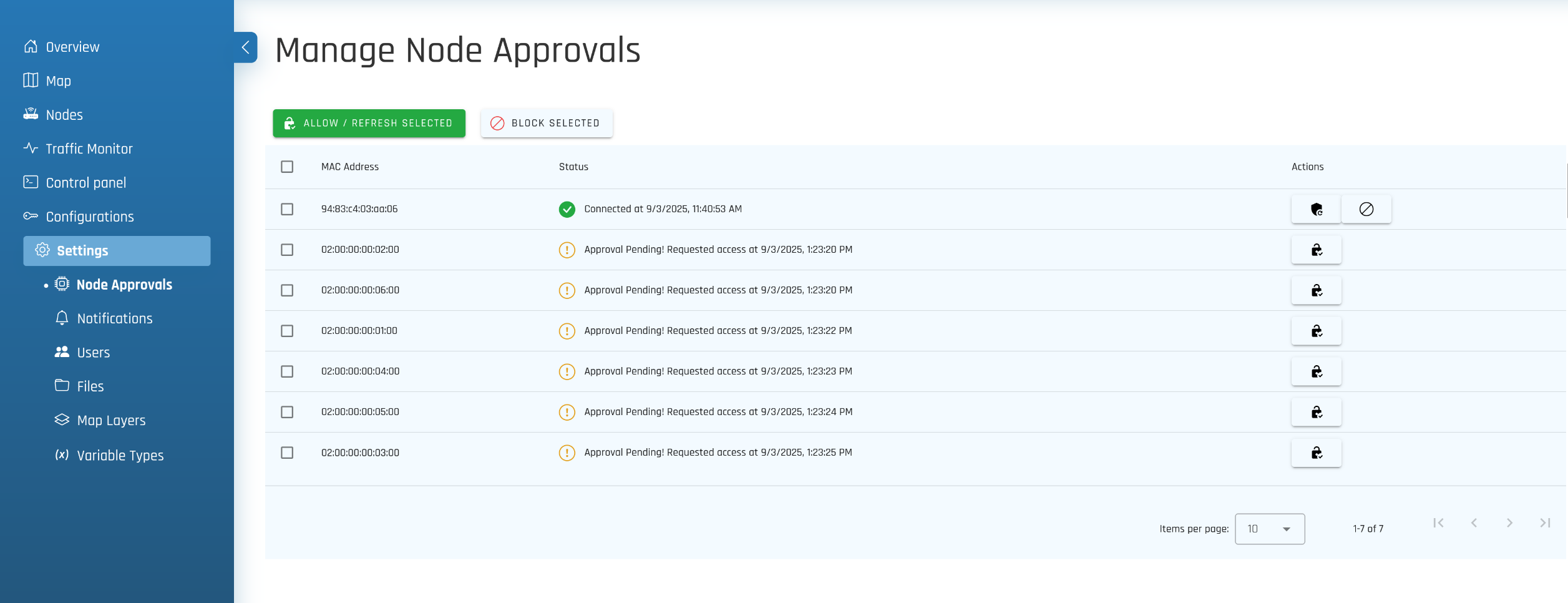
- Approve the device from your Hive UI.
- Log in to your Hive instance.
- Navigate to Settings > Node Approvals.
- Locate the device by its MAC address in the list of pending approvals.
- Click Approve to allow the device to connect.
- The device status will soon show Connected. It will appear in the Nodes list as connected.
TIP: See the Troubleshooting section if the device does not show up in Hive.
¶ Troubleshooting
¶ 1. Internet Connectivity
Make sure the device is connected to the Internet. Try to ping an Internet IP such as 1.1.1.1 or 8.8.8.8 to see if the IPs are reachable. If not, check your network configuration to make sure the device can actually reach the Internet. Typical issues
¶ 2. DNS Resolution
Make sure the device can resolve the Hive domain name. Try to ping the Hive domain. If it cannot resolve the name to an IP, check your DNS configuration. Usually, DNS is configured automatically through DHCP. Alternatively, it has to be configured manually.
¶ 3. Blocked Ports
The devices communicate with the Hive server with MQTT and HTTP. Make sure the following ports are reachable: 8883 (encrypted MQTT), 80 (HTTP), and 443 (HTTPS).
You can check that the ports are reachable using telnet. If it connects, just press Enter twice to see if you get a response. It should look like this:
# telnet $NAME.hive.meshmerize.net 8883
Trying x.x.x.x...
Connected to $NAME.hive.meshmerize.net.
Escape character is '^]'.
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
Connection: close
400 Bad RequestConnection closed by foreign host.The error “Bad Request” is returned because we didn't send a valid HTTP request. But this is enough to prove the connection could be established and data could be sent in both directions.
If this doesn't work, then there is probably a firewall blocking the port.
- Check the firewall configuration on the device to make sure outgoing connections are not blocked.
- Check with your network administrator to ensure your network is allowed to reach out to these ports.
- Sometimes ISPs (especially mobile ISPs) block port 8883. In this case, you can use the Hive domain
$NAME.mqtt.meshmerize.netwith port 443 as the MQTT Port.
¶ 4. TLS Issues
Ensure that TLS encryption works with the device. To verify this, you can
Typical issues with TLS are:
- The time is not correctly set on the device. TLS certificates are only valid for a specific time frame. If the time on the device is incorrect, the certificates will be rejected.
- Your network does TLS interception. Ask your network administrator if TLS interception is set up in your network. If it is, you need to install your certificate on the device.
As an insecure workaround, you can enable Skip TLS Validation in the Hive Worker settings.